Pan-cancer analysis uncovers a new class of promising CAR T–cell immunotherapy targets
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – May 03, 2024) Targeting anti-cancer therapy to affect cancer cells but not healthy cells is challenging. For chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T–cell immunotherapy, where a patient’s own immune cells are re-engineered to attack cancer cells, many solid and brain cancers lack an effective target. St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists have identified […]
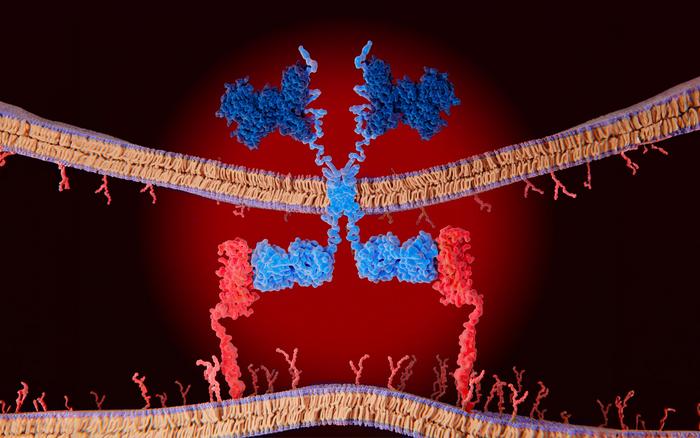
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – May 03, 2024) Targeting anti-cancer therapy to affect cancer cells but not healthy cells is challenging. For chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T–cell immunotherapy, where a patient’s own immune cells are re-engineered to attack cancer cells, many solid and brain cancers lack an effective target. St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists have identified 156 potential targets through a comprehensive analysis paired with an experimental validation in vivo. The findings were published today in Nature Communications.
Credit: St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – May 03, 2024) Targeting anti-cancer therapy to affect cancer cells but not healthy cells is challenging. For chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T–cell immunotherapy, where a patient’s own immune cells are re-engineered to attack cancer cells, many solid and brain cancers lack an effective target. St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists have identified 156 potential targets through a comprehensive analysis paired with an experimental validation in vivo. The findings were published today in Nature Communications.
“We discovered targets for cancer immunotherapy, which hopefully can be translated in the future into curative approaches,” said co-corresponding author Stephen Gottschalk, MD, St. Jude Department of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Cellular Therapy chair. “We’ve given the field a large set of potential targets and validated at least one, COL11A1.”
While COL11A1 was one of the 156 targets identified that the researchers validated in mouse models, others showed promise in cell lines such as anti-fibronectin CAR T cells. Most targets have yet to be tested but are publicly available for other researchers to pursue.
“In addition to validating the selected targets, we have built a data resource for the community,” said co-corresponding author Jinghui Zhang, PhD, St. Jude Department of Computational Biology. “The final list is available in a web portal. Others can evaluate the evidence and pursue any of these targets.”
The portal, named SCE-Miner, is freely available on the St. Jude Cloud platform. External researchers can access the data and use the internal analysis tools to fuel their own research.
“Our portal empowers the users to explore these targets and the underlying data,” Gottschalk said. “Other scientists can say, ‘Is this target present in a particular pediatric cancer subtype?’ They can access that information in the Cloud and do their own analysis.”
Fishing for CAR T–cell targets
The researchers found COL11A1 and the other targets by comprehensively analyzing the subparts of genes called exons. When a gene is transcribed to RNA, only exonic regions are retained to form a mature product, which will be used as a template for protein translation. The researchers looked at whole transcriptome sequencing data of 1,532 pediatric tumor samples with 7,460 normal tissue samples, finding which exons were more highly selective or uniquely expressed in cancer cells than normal cells. Such cancer-specific exons can potentially be targeted by CAR T cells without causing harm to healthy cells. The final target list also includes several targets identified in previous analyses and are being pursued clinically, increasing confidence in the group’s analytical approaches.
The St. Jude method differs in several ways compared to previous CAR target searches. The sample size was much larger, and the study involved all major cancer types. Therefore, the candidate pool was expanded. To ensure the inclusion of all relevant candidates to CAR T targets, the researchers focused on proteins existing inside the membrane, a traditional approach, and those sitting on top of the membrane in a place called the extracellular matrix, which was unusual.
“Normally, groups looking for new CAR targets looked only at membrane-associated proteins,” Gottschalk said. “But one of our targets told us that we needed to broaden our criteria to include proteins of the extracellular matrix. Most of those proteins are not anchored to the cell, but it turns out they stick to the cell surface. When the CAR comes, it can still recognize that protein and kill the cancer cell.”
The researchers also found that some of these genes have different exons expressed inside them, resulting in a different version of a protein called an isoform. Think of a gene as a movie; an isoform would be like a director’s cut, with different scenes cut, extended or inserted while maintaining major similarities to the original. Cancer cells are prone to alternative splicing of exons, which creates isoforms, which the St. Jude analysis detected in a way that had been difficult in earlier screens.
“We used a more straightforward and robust analysis than prior approaches,” Zhang said. “We could see if a subset or all set of exons within a gene were differentiated between cancer and normal cells, which allowed us to evaluate cancer-specificity at the isoform versus gene level.”
Authors and funding
The study’s first authors are Timothy Shaw, Jessica Wagner and Liqing Tian of St. Jude. The study’s other authors are Francis O’Neil and Ching Lau, The Jackson Laboratory Cancer Center; Elizabeth Wickman, Suresh Poudel, Jian Wang, Robin Paul, Selene Koo, Meifen Lu, Heather Sheppard, Yiping Fan and Xin Zhou, St. Jude.
The study was supported by grants from the Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation, Cure4Cam Foundation, National Institutes of Health (1F31CA257757-01A, R01CA216391 and P30CA076292), Alliance for Cancer Gene Therapy, St. Jude’s Translational Immunology and Immunotherapy initiative, Moffitt Quantitative Science Team Science Grant, Bio2 Department Pilot, National Cancer Institute (P30CA021765) and ALSAC, the fundraising and awareness organization of St. Jude.
St. Jude Media Relations Contacts
Michael Sheffield
Desk: (901) 595-0221
Cell: (901) 379-6072
michael.sheffield@stjude.org
media@stjude.org
Rae Lyn Hartley
Cell: (901) 686-2597
raelyn.rushing@stjude.org
media@stjude.org
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital is leading the way the world understands, treats and cures childhood cancer, sickle cell disease and other life-threatening disorders. It is the only National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center devoted solely to children. Treatments developed at St. Jude have helped push the overall childhood cancer survival rate from 20% to 80% since the hospital opened more than 60 years ago. St. Jude shares the breakthroughs it makes to help doctors and researchers at local hospitals and cancer centers around the world improve the quality of treatment and care for even more children. To learn more, visit stjude.org, read St. Jude Progress, a digital magazine, and follow St. Jude on social media at @stjuderesearch.
Journal
Nature Communications
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Discovery of immunotherapy targets for pediatric solid and brain tumors by exon-level expression
Article Publication Date
3-May-2024
What's Your Reaction?

































