Otters, especially females, use tools to survive a changing world
Sea otters are one of the few animals that use tools to access their food, and a new study has found that individual sea otters that use tools — most of whom are female — are able to eat larger prey and reduce tooth damage when their preferred prey becomes depleted. Credit: Chris Law Sea […]
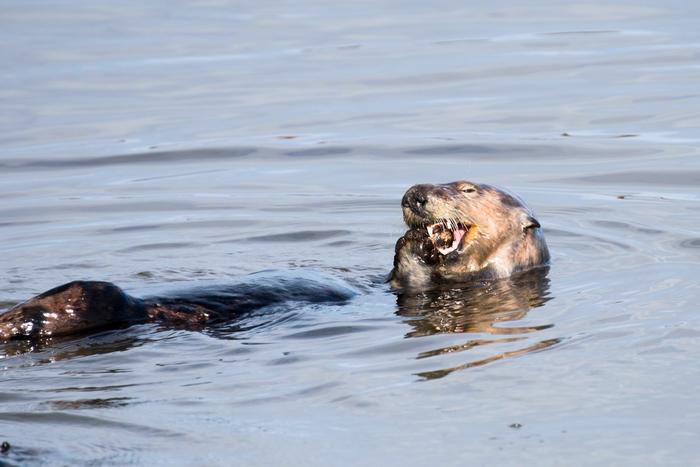

Sea otters are one of the few animals that use tools to access their food, and a new study has found that individual sea otters that use tools — most of whom are female — are able to eat larger prey and reduce tooth damage when their preferred prey becomes depleted.

Credit: Chris Law
Sea otters are one of the few animals that use tools to access their food, and a new study has found that individual sea otters that use tools — most of whom are female — are able to eat larger prey and reduce tooth damage when their preferred prey becomes depleted.
The study researchers and their enlisted volunteer “otter spotters” followed 196 radio-tagged southern sea otters off the coast of California to better understand how the threatened species uses tools in a rapidly changing environment. The research team from The University of Texas at Austin, University of California, Santa Cruz, Monterey Bay Aquarium and elsewhere monitored how the marine mammals used tools — such as rocks, shells and trash — to break open prey and identified links to the animals’ dietary patterns and dental health.
For the first time, researchers found that the use of tools among male and female otters led to a reduction in tooth injuries.
“Sea otters vary in how often they use tools,” said Chris Law, a postdoctoral researcher and an Early Career Provost Fellow at UT Austin who led the study while a graduate student at UC Santa Cruz. “The females are likely using tools to overcome their smaller body size and weaker biting ability in order to meet their calorie demands. Raising pups takes a lot of energy, and the females need to be efficient in their foraging. The study shows that tool use is an important behavior for survival.”
The study is published in Science.
In the southern sea otter’s range of coastal Central California, some of the preferred prey such as large abalone and sea urchins, are not difficult to break open. However, these food resources dwindle or disappeare in many areas. This leads otters to prey more often on crabs, clams, mussels and small marine snails whose hard shells can damage the otter’s teeth in the process of prying them open.
Tooth condition is important for survival because when an otter’s teeth become too worn or damaged, they could starve. Using tools helped individual otters to meet their calorie needs by branching out into different types of prey. The study found female otters had less tooth damage than male otters did.
Research shows that female otters are more likely to use tools, and in the study, those that did were able to access harder or larger prey than otters that did not use tools. In fact, females were able to consume prey that were up to 35% harder compared with that of males that used tools.
Female dolphins, chimps and bonobos are also known to use tools more than their male counterparts, probably for the same reasons. In these species, females tend to raise offspring, and they are often the ones that pass down tool-use behavior to offspring.
Listed as a threatened species under the U.S. Endangered Species Act, southern sea otters number only about 3,000 in California, where they play a critical role in marine ecosystems preying on sea urchins that feed on kelp forests.
Rita Mehta and Tim Tinker of the University of California, Santa Cruz; Jessica Fujii, Teri Nicholson and Michelle Staedler with the Monterey Bay Aquarium; Joseph Tomoleoni of the U.S. Geological Survey; and Colleen Young of the California Department of Fish and Wildlife were also authors on the paper. Chris Law was previously a postdoctoral scholar with University of Washington.
The research was funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation, Packard Foundation, Coastal Conservancy, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Pacific Gas & Electric and Bureau of Ocean Energy Management.
Journal
Science
DOI
10.1126/science.adj6608
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Tool use increases mechanical foraging success and tooth health in southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis)
Article Publication Date
17-May-2024
COI Statement
Authors declare no competing interests.
What's Your Reaction?