Estrogen receptor mutation study suggests potential treatments for endometrial cancers
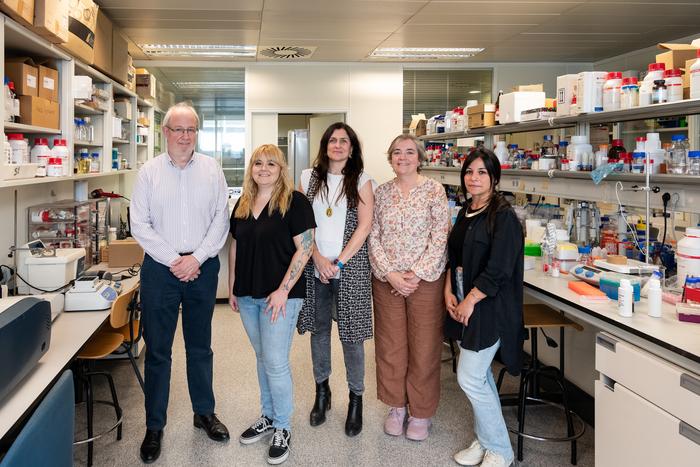
Researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute identified potential new treatment options for people with endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecological cancer and high levels of estrogen promote its development. The study, published in Molecular Cancer Research discovered that estrogen receptor mutations found in endometrial cancers cause large changes in endometrial cancer cells. Credit: Huntsman Cancer Institute Researchers at Huntsman Cancer […]

Researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute identified potential new treatment options for people with endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecological cancer and high levels of estrogen promote its development. The study, published in Molecular Cancer Research discovered that estrogen receptor mutations found in endometrial cancers cause large changes in endometrial cancer cells.

Credit: Huntsman Cancer Institute
Researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute identified potential new treatment options for people with endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecological cancer and high levels of estrogen promote its development. The study, published in Molecular Cancer Research discovered that estrogen receptor mutations found in endometrial cancers cause large changes in endometrial cancer cells.
Estrogen is a reproductive hormone that binds and activates estrogen receptors. Cancer can cause estrogen receptors to remain in a state of constant activity. That increases shedding of the endometrial lining. “Our goal was to characterize estrogen receptor mutations in endometrial cancer to see how they affected gene expression, along with how these mutations made cells more aggressive and fast-growing,” says Zannel Blanchard, PhD, postdoctoral fellow at Huntsman Cancer Institute and lead investigator on the study. “We found that the mutations caused large changes in gene expression and cellular behavior.”
The team used their findings to identify potential treatments for endometrial cancers with high levels of estrogen receptor activity. They found that inhibitors of CDK9, a protein that works with estrogen receptors, were effective at reducing the growth and aggressiveness of endometrial cancer cells.
“Besides surgery to treat endometrial cancer, there’s only one drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating primary endometrial cancer, and it was approved in the 1970s,” says Jay Gertz, PhD, the senior author and researcher at Huntsman Cancer Institute and associate professor of oncological sciences at the University of Utah. “Our results help us to really start moving toward personalized—or precision—medicine for endometrial cancer.”
The study was presented to a breast and gynecologic cancer research advocacy group made up of patients. Participants volunteer their time and meet once a month at Huntsman Cancer Institute.
“We can write support letters to help with upcoming research grants and offer a patient perspective to researchers,” says Deb Jordan, an endometrial cancer patient at Huntsman Cancer Institute and advocacy group participant. “We also get to hear about the ongoing research at Huntsman Cancer Institute. That puts my mind at ease, to learn all that is being done for endometrial cancer.”
“It’s exciting because the study suggests that there may be more options for endometrial cancer patients,” says Blanchard. “There’s more going on when you look deeper and we get to share these findings with patients who have been through treatment.”
Gertz says the treatment options for endometrial cancer are limited and patients play an important role in inspiring researchers to find new therapies. “It really motivates me and my lab to understand the disease better and find new treatments.”
The study suggests that molecular evaluation of tumors could lead to more personalized treatment options for endometrial cancer patients.
This study was supported by the Department of Defense and National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute, including P30 CA042014 and Huntsman Cancer Foundation.
About Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah
Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U) is the official cancer center of Utah and the only National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center in the Mountain West. The institute is leading the world in scientific discovery, and turning it into unsurpassed cancer care, transforming hope into a reality. Huntsman Cancer Institute focuses on delivering a cancer-free frontier to Utah, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, and Wyoming (The Area We Serve). Huntsman Cancer Institute is home to over 300 clinical trials, with over 237 research teams studying cancer at any given time and more genes for inherited cancers have been discovered at Huntsman Cancer Institute than at any other cancer center. Huntsman Cancer Institute’s scientists are world renown for understanding how cancer begins and using that knowledge to develop innovative approaches to treat each patient’s unique tumor. Huntsman Cancer Institute was founded by Jon M. and Karen Huntsman.
Journal
Molecular Cancer Research
DOI
10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-22-0848
Article Publication Date
19-Jul-2023
What's Your Reaction?