Alzheimer’s disease not forgotten as FDA oversees record number of designations awarded
The FDA has seen a record surge in review designations being awarded over the last two years for Alzheimer’s indications,…
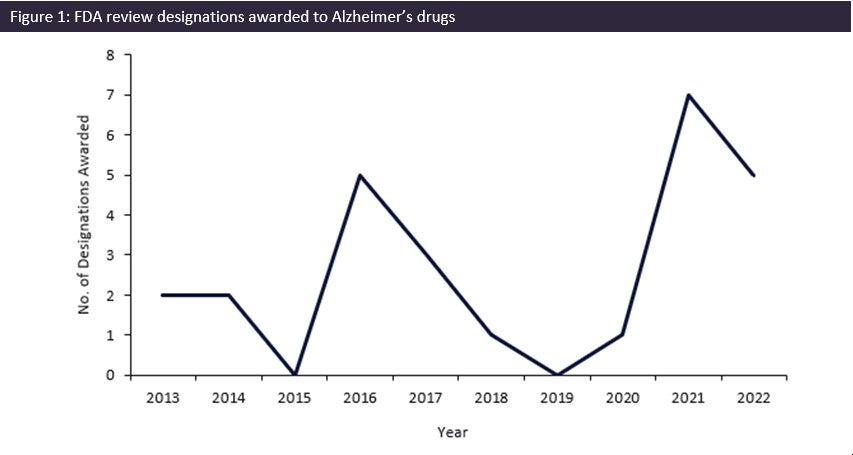
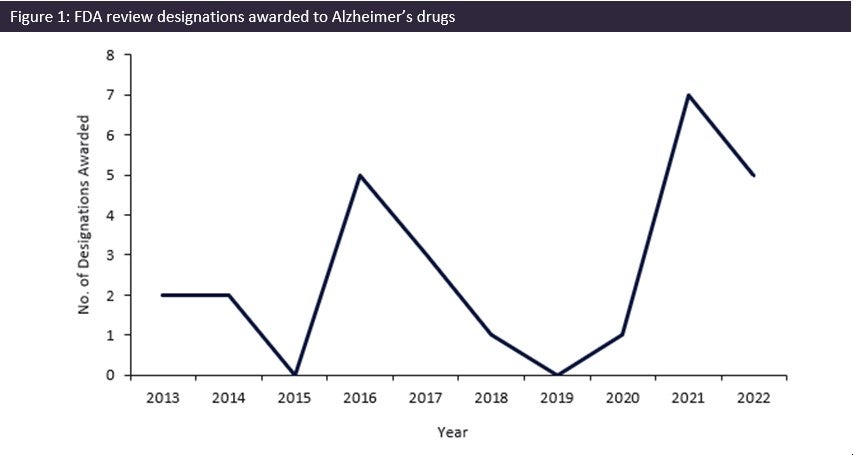
The FDA has seen a record surge in review designations being awarded over the last two years for Alzheimer’s indications, with 12 review designations being awarded to drugs between 2020 and 2022. This coincided with the much-anticipated wave of monoclonal antibody drugs for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) such as Eisai/Biogen’s Leqembi (lecanemab-irmb) and Eli Lilly’s donanemab, which are predicted to provide significant improvement on previous AD therapies.
AD is the leading cause of dementia, which is an umbrella term for a series of syndromes that can lead to memory loss, cognitive decay, and behavioural change. AD currently affects more than 55 million people in the world. It is also an area of significant unmet need. According to GlobalData’s drug database, there are more than 300 drugs currently marketed for AD, but they often only treat the symptoms and do not halt or reverse the disease itself. This unmet need will increase as the number of elderly people (older than 65 years of age) within the global population continues to grow. The development of novel and effective drugs is of special importance. As such, the usage of review designations such as Breakthrough Therapy, Accelerated Approval, Fast Track Designation, and Priority Review will be needed in promoting and speeding up the development of these drugs.
©GlobalData.
As seen in Figure 1, the FDA has taken this unmet need seriously and has significantly increased the number of drugs for AD being awarded review designations. Between 2020 and 2021, the number of designations increased by 600%, with seven designations being awarded by the FDA in 2021. This was the greatest number of designations awarded in the last ten years and was 40% greater than the previous peak of five designations in 2016. Roche’s gantenerumab, Biogen/Eisai’s Lequmbi, and Eli Lilly’s donanemab, all monoclonal antibody drugs, were among these seven designations. Leqembi was awarded Fast Track, Accelerated Approval, and Breakthrough Therapy designation, and has been approved as a novel AD drug as it demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in cognitive decline in patients treated with Leqembi.
The significant increase in the number of review designations awarded by the FDA over the last two years shows that there is a concerted effort to support and promote the development of novel AD drugs to treat this ever-growing disease. Key successes of the FDA’s efforts include the quick development of Leqembi. Five designations were awarded in 2022, and it is GlobalData hopes that this level of awarded designations is maintained in 2023 to help combat and support the treatment of AD.
What's Your Reaction?

































